Cloud software for enterprises is revolutionizing the way businesses operate by offering scalable and flexible solutions tailored to meet complex organizational needs. As digital transformation accelerates, enterprises are turning to cloud technologies to enhance their operational efficiency, foster collaboration, and drive innovation. With a myriad of cloud software options available, understanding their significance and benefits is crucial for organizations looking to improve their overall performance.
This overview will delve into the essential features of cloud software, explore various deployment models, and address critical security considerations. By examining real-world applications and emerging trends, enterprises can strategically adopt cloud solutions to navigate the future landscape of business technology.
Overview of Cloud Software for Enterprises
Cloud software has emerged as a cornerstone for enterprises striving for agility and efficiency in their operations. It refers to applications and services delivered over the internet, enabling businesses to use software solutions without the need for extensive on-premises infrastructure. The significance of cloud software in enterprise environments lies in its ability to enhance collaboration, streamline processes, and facilitate data-driven decision-making.
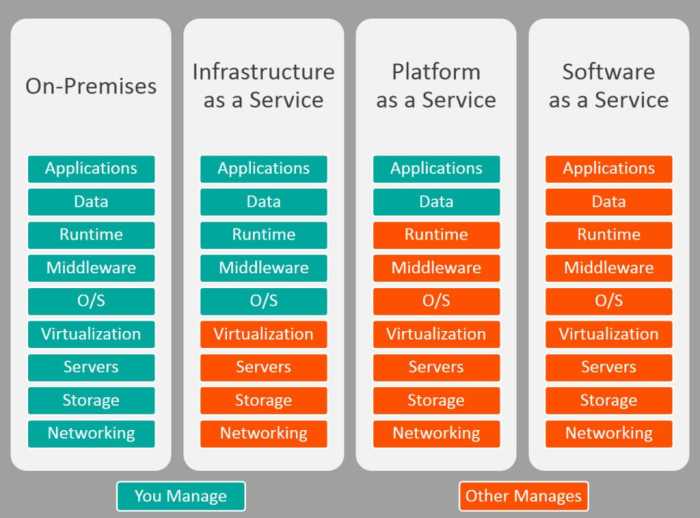
The types of cloud software available for enterprises can be broadly categorized into three main types: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). SaaS provides ready-to-use applications over the internet, PaaS offers a platform for developing, testing, and deploying applications, while IaaS delivers virtualized computing resources. Each type addresses different enterprise needs, allowing organizations to choose solutions that align with their specific goals.
Adopting cloud solutions offers key benefits for large organizations, including cost savings, scalability, and enhanced collaboration. By migrating to cloud software, enterprises can reduce their IT overhead, leverage on-demand resources, and enable cross-functional teams to work together seamlessly, regardless of geographical barriers.
Features and Functions

Essential features of cloud software for enterprise needs include user-friendly interfaces, robust security protocols, and extensive integration capabilities. Additionally, the ability to provide real-time analytics and reporting is crucial for enterprises seeking to make informed decisions based on data.
Functionalities that enhance operational efficiency in enterprises involve automation tools, workflow management systems, and cloud-based project management solutions. These functionalities allow organizations to streamline their processes, minimize human error, and improve overall productivity.
Scalability and flexibility are paramount in cloud software. As enterprises grow, their software needs evolve, necessitating solutions that can easily adapt to changing demands. Cloud software enables organizations to scale resources up or down based on actual usage, ensuring optimal performance without incurring unnecessary costs.
Cloud Deployment Models
There are several cloud deployment models that enterprises can consider: public, private, hybrid, and multi-cloud. Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party providers, offering resources and services over the internet, making them cost-effective for many businesses. Private clouds, on the other hand, are dedicated to a single organization, providing enhanced security and control.
Hybrid clouds combine elements of both public and private clouds, allowing enterprises to manage sensitive data in a private environment while leveraging the scalability of public resources. Multi-cloud strategies involve using multiple cloud services from different providers, helping enterprises avoid vendor lock-in and choose the best solutions for their needs.
Each deployment option presents distinct impacts on security and compliance requirements. For instance, while public clouds may expose enterprises to higher risks, private clouds can provide enhanced security protocols to meet regulatory standards. Scenarios such as a financial institution requiring strict compliance might favor a private cloud, while a tech startup could benefit from the flexibility of a public cloud solution.
Security Considerations
Common security challenges associated with cloud software in enterprises include data breaches, compliance violations, and inadequate access control. These challenges necessitate robust security measures to protect sensitive information and maintain regulatory compliance.
Implementing strong security measures in cloud environments involves several guidelines, including the use of multi-factor authentication, regular security audits, and employee training on cybersecurity best practices. Organizations must also ensure that their cloud service providers adhere to industry standards and certifications.
Data encryption and access controls play a critical role in protecting sensitive information. Encrypting data both at rest and in transit helps to secure it from unauthorized access, while strict access controls ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information.
Integration with Existing Systems

Seamless integration of cloud software with existing IT infrastructure is vital for enterprises. This integration allows organizations to leverage their current investments while transitioning to cloud solutions without disruption.
Common integration challenges may include data incompatibility, lack of interoperability between systems, and the complexity of migrating legacy applications. Addressing these challenges often requires careful planning and the use of integration platforms that facilitate smooth connections between on-premises and cloud-based systems.
To ensure data consistency across integrated systems, enterprises can employ strategies such as data synchronization tools and middleware solutions. These methods help to maintain accurate and up-to-date information across all platforms, supporting effective decision-making and operational efficiency.
Cost Implications, Cloud software for enterprises
Adopting cloud software can have significant financial implications for enterprise operations. Initial investments may be lower than traditional software solutions, but ongoing costs must be assessed to understand the total cost of ownership.
Potential cost savings from cloud solutions include reduced hardware expenditures, lower maintenance costs, and the ability to pay only for what is used. A detailed analysis should compare these potential savings against the costs associated with traditional software licensing, including upgrades and support.
| Cost Factors | Cloud Software | Traditional Software |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Setup Costs | Lower | Higher |
| Maintenance Costs | Minimal | Ongoing |
| Scalability Costs | Pay-as-you-go | Fixed |
| Upgrade Costs | Included | Additional Fees |
Vendor Selection Criteria
When evaluating cloud software vendors, enterprises should consider several criteria, including the provider’s reputation, service offerings, and technological capabilities. Assessing the vendor’s track record in delivering reliable solutions is essential for making informed decisions.
Vendor support and service level agreements (SLAs) are also critical factors. A strong SLA ensures that the provider commits to certain performance metrics, response times, and support levels, which can significantly impact the success of the cloud transition.
Choosing between established vendors and emerging cloud providers presents both pros and cons. Established vendors often provide proven solutions and extensive support networks, while emerging providers may offer innovative features and competitive pricing. Evaluating the specific needs of the organization will guide this decision.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications

Success stories of enterprises effectively implementing cloud software abound, demonstrating the transformative power of these solutions. For instance, a major retail chain utilized cloud-based inventory management software to streamline operations, resulting in a 25% reduction in stockouts and improved customer satisfaction.
Conversely, lessons learned from failures in cloud software adoption often highlight the importance of thorough planning and change management. A financial services firm that rushed its cloud migration experienced significant downtime and data loss, emphasizing the need for a well-structured strategy.
Several industries actively leverage cloud solutions, including:
- Healthcare: Enhanced patient data management.
- Finance: Improved compliance tracking and reporting.
- Retail: Streamlined supply chain operations.
- Manufacturing: Optimized production schedules and resource allocation.
- Education: Facilitated remote learning and collaboration.
Future Trends in Cloud Software
Emerging trends and technologies are shaping the future of cloud software for enterprises. One significant trend is the increasing integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities, allowing organizations to harness data for predictive analytics and enhanced decision-making.
The potential impact of edge computing is also noteworthy, as it enhances cloud service delivery by processing data closer to the source. This reduces latency, improves response times, and enables real-time processing, making it particularly beneficial for industries that require immediate insights.
As these trends continue to evolve, enterprises must stay informed and adapt their cloud strategies to leverage new technologies effectively, ensuring they remain competitive in an increasingly digital landscape.
Outcome Summary: Cloud Software For Enterprises
In conclusion, the adoption of cloud software for enterprises not only streamlines operations but also positions organizations to adapt to future challenges with agility and resilience. By carefully considering deployment models, security measures, and vendor selection, enterprises can leverage cloud solutions to enhance their competitiveness in an increasingly digital world. As innovations continue to emerge, staying ahead in the cloud technology realm will be key to sustained success.