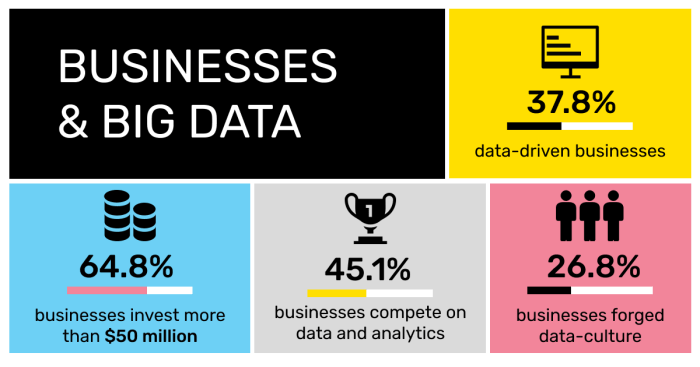
big data for business sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. As organizations gather and analyze vast amounts of data, the significance of big data has become increasingly clear in today’s fast-paced business environment. It’s not just about the volume of data, but also the velocity, variety, and veracity that define it, shaping how companies operate and compete in their respective markets.
Through the evolution from traditional data management to sophisticated analytics, big data empowers businesses to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and enhance customer experiences. In this landscape, understanding the characteristics that categorize data as ‘big’ is essential for leveraging its full potential.
Introduction to Big Data: Big Data For Business
In the contemporary business landscape, big data has emerged as a crucial asset that drives strategic decision-making and operational efficiency. Big data refers to vast, complex datasets that traditional data processing software cannot manage effectively. Its significance lies in its ability to provide valuable insights that can enhance business performance and foster innovation.
Data is categorized as ‘big’ based on several characteristics, often referred to as the “3 Vs”: Volume, Velocity, and Variety. Volume pertains to the massive amounts of data generated every second; velocity addresses the speed at which data is created and processed; and variety encompasses the different types of data, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured formats. Over time, the evolution of big data has transitioned from traditional data management systems, which relied on structured data, to advanced analytics and machine learning applications that handle diverse data formats and real-time processing.
Benefits of Big Data for Business
The integration of big data analytics in business operations significantly enhances decision-making processes. Through comprehensive data analysis, organizations can identify trends, forecast outcomes, and make data-driven decisions that minimize risks.
Cost savings represent another significant advantage of big data analytics. By leveraging big data, companies can optimize their operations, reduce waste, and improve resource allocation, resulting in substantial financial benefits. For instance, retailers use big data to analyze customer preferences and adjust inventory levels accordingly, thereby reducing overhead costs.
Several organizations have successfully harnessed the power of big data for competitive advantage. One notable example is Netflix, which employs data analysis to tailor content recommendations based on viewer preferences, boosting user engagement and retention.
Big Data Technologies and Tools
Key technologies play an essential role in the management of big data. Hadoop and Apache Spark are two prominent frameworks widely used for storing and processing large datasets. Hadoop provides a distributed storage system that allows organizations to manage vast amounts of data efficiently, while Spark offers powerful in-memory processing capabilities that enhance speed and performance.
| Tool | Features |
|---|---|
| Hadoop | Distributed storage and processing, fault tolerance, scalability |
| Spark | In-memory processing, real-time analytics, support for various data sources |
| Tableau | Data visualization, interactive dashboards, user-friendly interface |
| Apache Flink | Stream processing, batch processing, state management |
Cloud computing has revolutionized big data storage and processing by offering scalable and flexible solutions. Cloud platforms enable businesses to store large volumes of data securely while providing the computational power necessary for advanced analytics.
Implementing Big Data Strategies
Developing a comprehensive big data strategy involves several critical steps. Organizations must first assess their data needs and capabilities, identify key objectives, and select appropriate technologies that align with their goals.
Data governance and compliance are paramount in big data initiatives. Establishing clear policies for data management, privacy, and security ensures that organizations adhere to regulations while maximizing the value of their data assets.
However, challenges such as data quality, integration difficulties, and a lack of skilled personnel can hinder the implementation of big data solutions. Businesses can overcome these obstacles by investing in training, fostering a data-centric culture, and utilizing automated tools for data management.
Use Cases of Big Data in Different Industries

Big data’s application spans across various industries, each leveraging it to drive innovation and efficiency. In healthcare, for instance, big data aids in predictive analytics for patient care, enabling doctors to make informed decisions based on historical data and trends.
In the finance sector, institutions utilize big data for fraud detection and risk assessment, enhancing security and trust. Retailers apply big data insights to optimize supply chains and enhance customer experiences through personalized marketing strategies.
– Healthcare: Predictive analytics for patient outcomes.
– Finance: Real-time fraud detection and risk management.
– Retail: Personalized shopping experiences and inventory optimization.
The impact of big data on customer experience and engagement is profound, offering insights that enable businesses to tailor their offerings and enhance satisfaction.
Future Trends in Big Data
Emerging trends in big data include the integration of artificial intelligence, which enhances predictive analytics and automation. Real-time analytics is also gaining traction, allowing organizations to make instantaneous decisions based on current data.
Ethical considerations and data privacy are becoming increasingly critical as businesses navigate the complexities of big data practices. Organizations must prioritize ethical data usage and transparency to maintain customer trust.
To prepare for future developments in big data technology, businesses should invest in advanced analytics capabilities, foster a culture of continuous learning, and stay informed about emerging trends and regulations.
Skills and Roles in Big Data, Big data for business

Professionals working in the big data landscape require a diverse skill set that includes data analysis, programming, and an understanding of machine learning algorithms. Core competencies such as statistical analysis and data visualization are also essential.
Common roles found in big data teams include data scientists, who analyze and interpret complex data; data engineers, responsible for building and maintaining data architecture; and business analysts, who bridge the gap between data insight and strategic business objectives.
Continuous learning and adaptation are vital in this evolving field. As technology and methods advance, professionals must stay updated with the latest tools and trends to remain competitive.
Closing Summary

In summary, the journey through the realm of big data for business highlights its transformative power, from driving strategic decisions to revolutionizing entire industries. As organizations continue to confront challenges in implementing big data solutions, the key lies in developing effective strategies, embracing emerging technologies, and fostering a culture of continuous learning. Looking ahead, businesses that adeptly navigate the evolving big data landscape will not only survive but thrive in an increasingly data-driven world.